N-Acetyl-L-Aspartic acid
N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid, abbreviated as NAA, is second most abundant molecule in nervous systems after amino acid glutamate. It is synthesized in brain from aspartic acid and acetyl co-enzyme A. It also acts as nutrient.
Manufacture
In a biological process, NAA is produced from rat brain acetone. Commercially, it is manufactured by acetylation of L-aspartic acid bis(trimethylsilyl)ester using acetyl chloride.
| Synonyms |
N-Acetyl aspartate
NAA |
| CAS no. |
997-55-7 |
| EINECS no. |
213-643-9 |
| Molecular formula |
C6H9NO5 |
| Molecular weight |
175.14 |
| Structure |
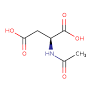 |
Applications in Synthesis
| The chiral acid is used to synthesize: |
| Its anhydride |
| Homoserine gamma-lactones |
Other Applications
| As reagent in selective reductions of cyclic ketones |
| In acid-catalyzed cyclization reactions |
| In peptide synthesis |
| As a nutraceutical supplement in capsule, tablet, and liquid dosage form |
| As antioxidant |
| As human and rat metabolites |
| Isotopic form used in studies for metabolic alteration associated with schizophrenia |
SPECIFICATIONS
| Test |
Unit |
Specification |
| Appearance |
– |
White powder |
| Specific rotation (C = 1, HAc) |
Degree |
50.0 – 54.0 |
| Water |
% |
Max 0.5 |
| Assay |
% |
Min 98.0 |
STORAGE
The product is stored at ambient temperature.
PACKING
25 kg Fibre drum.
REACH Status
Not Registered yet.